Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can pose serious health risks when present in high concentrations indoors. To manage and reduce radon levels, homeowners often use radon test kits and radon mitigation systems. While both are essential for ensuring safe radon levels, the home inspection professionals at HomePro Inspections want to help you understand the distinct roles of radon test readings and the manometer in a radon mitigation system.
One common question we often receive is, “Why is the reading from the radon test different from the reading on the radon mitigation system?” The answer is that it has to do with the fact that they represent two entirely different measurements. Let me explain.
Radon Test Reading
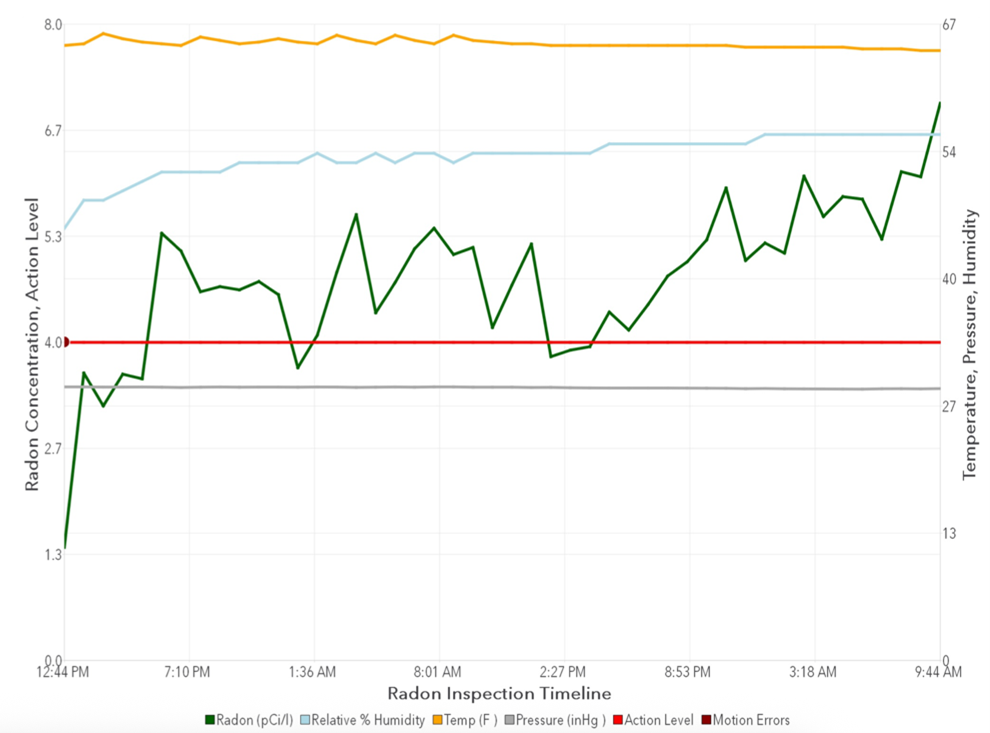
Radon test readings measure the actual concentration of radon gas in the air, expressed in picocuries per liter (pCi/L). These readings provide direct insight into whether radon levels are within safe thresholds, typically set by regulatory authorities like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States. The EPA recommends taking action if radon levels exceed 4 pCi/L, although levels below this are still advised to be reduced whenever feasible.
Electronic Continuous Radon Monitor (CRM)
How Radon Tests Work
Radon tests can be conducted using short-term or long-term methods.
· Short-term tests typically measure radon levels over a span of 2 to 7 days, utilizing activated charcoal kits or electronic continuous radon measurement devices. HomePro Inspections employs CRM devices for real estate transactions.
· Long-term tests offer a more accurate average of radon levels over a period of 90 days to a year, providing a better understanding of seasonal variations.
Purpose of Radon Test Readings
Radon test readings are used primarily to:
· Identify if mitigation efforts are necessary.
· Monitor radon levels over time to ensure ongoing safety.
· Verify the effectiveness of an existing radon mitigation system.
Radon test readings plotted over time
Passive versus Active Mitigation System
There are two types of radon mitigation systems: passive and active. A passive system consists of a vertical vent pipe that runs from a sub-slab collection point, through the conditioned space of the home, and out through the roof. There is no fan in the system; it relies on the natural "stack effect" to draw soil gases up and out of the house.
An active mitigation system, while employing the same components as a passive mitigation system, utilizes a radon vent fan to “actively” pull air from beneath the structure. Generally, if a passive system cannot safely mitigate indoor radon levels, a radon vent fan can be added to convert it to an active system.
Manometer on a Radon Mitigation System
A manometer, usually seen as a U-shaped or digital gauge, is a vital part of an active radon mitigation system. Unlike radon test readings, the manometer does not measure radon concentration. Instead, it monitors the pressure differential created by the system's fan to ensure it operates properly.
A manometer on an active radon mitigation system
How a Manometer Works
The manometer measures the suction or pressure generated by the mitigation fan, typically in inches of the water column. This pressure is essential for drawing radon gas from beneath a building's foundation and safely venting it above ground. A properly functioning mitigation system will show consistent readings on the manometer, indicating that the fan is working.
Purpose of the Manometer
The manometer serves the following purposes:
· Confirms that the radon mitigation system is active and generating suction.
· Alerts homeowners to potential issues, such as fan failure or blockages in the vent system.
· Provides a visual reference for maintaining system performance.
Key Differences Between Radon Test Readings and the Manometer
· Measurement Focus—Radon test readings measure radon levels in the air, while the manometer measures pressure differences within the mitigation system.
· Function—Radon test readings assess the presence of radon, whereas the manometer monitors the operational status of the mitigation system.
· Usage—Radon test readings are conducted periodically to evaluate safety, while the manometer provides continuous monitoring of system functionality.
Summary
Both the radon test readings and the manometer play critical roles in managing indoor radon levels, yet they have distinct functions. Radon test readings ensure that radon concentrations remain within safe limits, while the manometer serves as a system health indicator, confirming that the mitigation system effectively reduces radon gas. Understanding these differences empowers homeowners to maintain a safe and healthy living environment while confidently addressing radon concerns.
At HomePro Inspections, our home inspectors are trained to identify and report any potential issues they may encounter. Any problems are documented in your home inspection report and recommended for resolution by a qualified professional.
Visit our website to learn more or to schedule your home inspection in the Rochester, Owatonna, and Faribault, MN areas. You can contact us today at (507) 202-8942, send us an email, or utilize our online “Schedule Now” feature to set up an appointment.